Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) therapy represents a groundbreaking advancement in depression treatment, particularly for individuals unresponsive to traditional methods. This non-invasive procedure uses magnetic pulses to stimulate specific brain regions linked to mood regulation. TMS offers several benefits, including minimal side effects, no need for anesthesia, and the ability to resume daily activities immediately after sessions. Research supports its effectiveness in reducing depressive symptoms and improving overall mental health. As awareness grows, TMS is becoming a promising option within personalized mental health care, providing hope for those seeking alternative treatments to overcome the challenges of depression and achieve lasting recovery.
What is TMS Therapy?
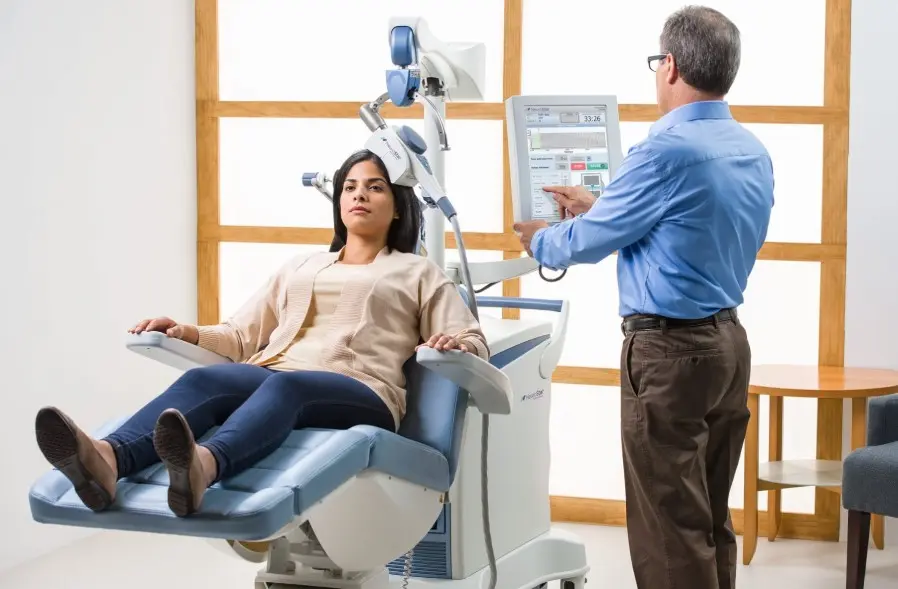
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) therapy is revolutionizing the approach to treating depression, standing as a beacon of hope, particularly for those who haven’t responded favorably to traditional methods like medication or talk therapy. This engaging treatment employs magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain’s regions responsible for mood regulation. As more individuals explore TMS therapy in Utah, it’s becoming evident how profoundly it can impact mental well-being by offering a new perspective on treatment.
TMS involves placing a coil gently against the patient’s scalp, primarily near the forehead. An important part is the coil, which stimulates particular brain areas linked to depression by sending focused magnetic pulses. Unlike medication, which systematically affects the entire body, TMS focuses locally, which might help explain its efficacy in alleviating depressive symptoms. With treatments varying in duration, patients typically attend sessions five days a week, each lasting 30 to 40 minutes over four to six weeks. This commitment is crucial for experiencing the full benefits of therapy.
Mechanics Behind TMS
The science underlying TMS is both fascinating and complex. TMS alters brain chemistry by transmitting magnetic pulses in subtle yet impactful ways. It stimulates activity in the prefrontal cortex, which is often underactive in individuals with depression. This stimulation is thought to enhance neural connectivity and normalize function, improving mood. Unlike its more invasive counterpart, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), TMS does not require anesthesia, nor does it cause memory loss or seizures, making it a more appealing option for many.
Scientific Backing
A wealth of scientific study buoys the efficacy of TMS. Various clinical trials and research have been conducted, producing a mosaic of evidence supporting its effectiveness as a treatment. For example, collectively, studies have suggested that over half the patients treated with TMS report a marked reduction in their depression symptoms, and for some, these effects lead to complete remission. This demonstrates TMS’s opportunity as a viable alternative when conventional treatments fall short. As the scientific community keeps investigating and verifying TMS, confidence in its application only grows stronger.
Addressing Common Concerns
Considering TMS therapy often elicits a range of questions and concerns from prospective patients. Here’s an attempt to address some of the most common inquiries:
- Who is eligible for TMS?Typically, TMS is recommended for adults diagnosed with major depressive disorder who have not achieved desirable outcomes with antidepressant medications or prefer to avoid them due to side effects.
- What side effects might occur?Fortunately, TMS is noted for its mild side effect profile, primarily because it doesn’t involve medication. Some individuals might experience temporary scalp discomfort or mild headaches, which dissipate as treatment progresses.
- Does insurance cover TMS?Over the years, insurance companies have increasingly recognized TMS as a necessary part of depression care protocols, making it more accessible for patients. Still, coverage varies, and patients must verify their specific plans to avoid unexpected expenses.
Contrasts with Traditional Treatments
TMS stands out from other depression treatments due to its non-invasive and localized approach. Unlike antidepressants, which alter neurochemical balance throughout the entire body, TMS directs its focus on the brain’s specific area implicated in mood disorders. The side effect profile is markedly different, often making TMS a preferable option for those who have endured the adverse impacts of medications, such as weight gain, fatigue, or sexual dysfunction. While both medications and TMS offer paths to wellness, the absence of systemic effects with TMS provides a compelling reason for its consideration.
Personal Testimonials
Accounts of those who have embarked on the TMS journey provide profound insights into its possible life-altering effects. Many patients recount feelings of hope restored and daily functioning enhanced, painting a picture of lives reinvigorated through this therapy. Personal testimonials often describe transformative experiences with TMS, where conventional treatments failed. According to numerous reports, patients describe mood improvements and a return to activities and interests, suggesting holistic enhancements to their quality of life.
The Evolution of TMS
The world of TMS therapy is ever-expanding, continuously evolving as new research emerges. Not confined solely to depression, clinicians are exploring TMS’s potential in treating other mental health disorders such as anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). This broadening scope highlights the potential of TMS to serve as a versatile tool in mental health care, signaling a bright future for its role in holistic treatment approaches. As understanding of brain function is enhanced, so is the scope of TMS applications, indicating the innovative nature of this therapy.
Resources for Support
In tackling depression or any mental health condition, the paramount step is seeking support and learning about available treatment options like TMS therapy. Resources abound for those ready to take proactive measures in managing their mental health. Healthcare professionals can provide valuable guidance on treatment appropriateness, navigating insurance complexities, and accessing local TMS providers. A robust support network is vital in managing depression, reinforcing TMS’s integration into a comprehensive care plan as a successful strategy for many individuals.
Also Read-Tracking the Application of Tech that Transformed a Frowned-Upon Card Game into a Global Sensation